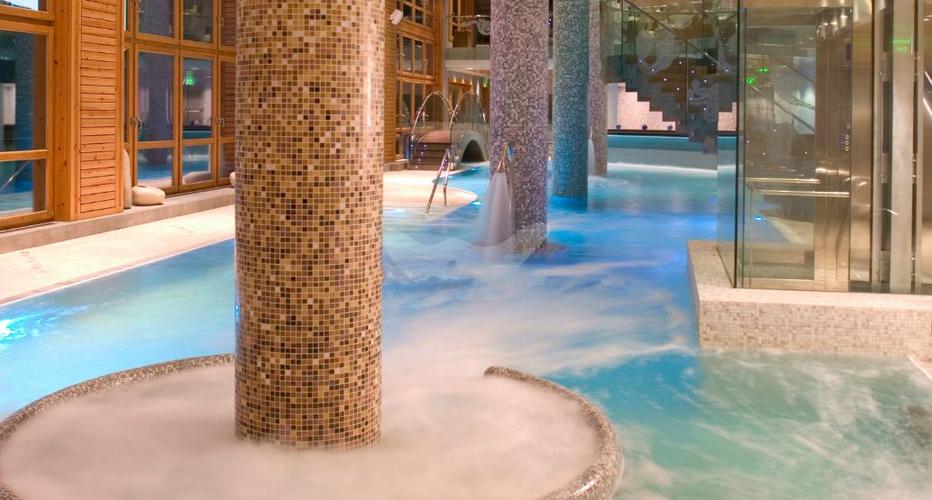
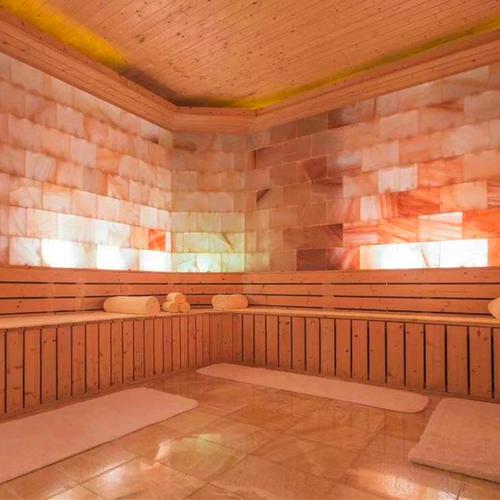
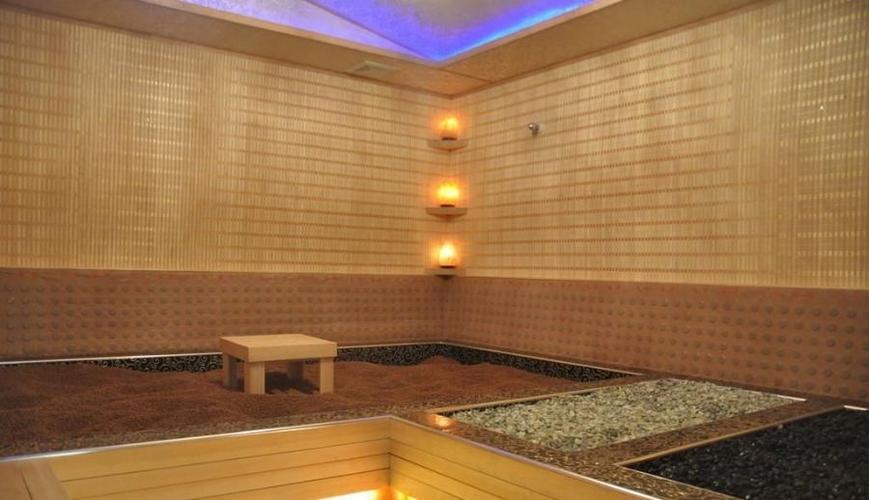
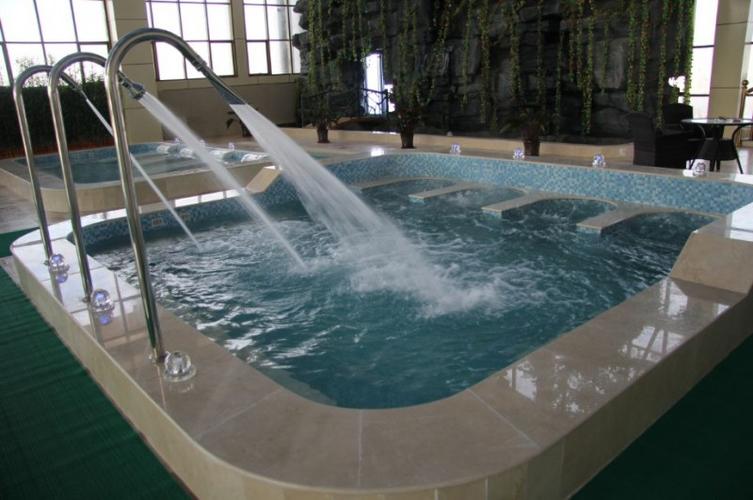
Sweat Therapy
Sweat therapy, often referred to as "汗蒸" in Chinese, is a practice that has been deeply ingrained in various cultures for centuries. It involves inducing profuse sweating through various methods, with the aim of promoting detoxification, relaxation, and overall well-being. While modern society often focuses on quick fixes and technological advancements, sweat therapy offers a timeless approach to health and wellness, rooted in ancient wisdom.
Historical Roots
The history of sweat therapy stretches back millennia, with evidence suggesting its use in ancient civilizations across the globe.
In ancient Greece, sweat baths, known as "laconica," were popular among athletes and the general population. The Greeks believed that sweating helped to cleanse the body of impurities and improve circulation. These baths were often built near natural hot springs and involved sitting or lying on heated stones while being drenched in hot water.
Similarly, the Romans embraced sweat baths, known as "balnea," as an integral part of their daily routines. Roman baths were elaborate structures featuring various pools, saunas, and steam rooms. The Romans believed that sweating helped to alleviate muscle soreness, improve skin health, and boost mental clarity.
In ancient China, sweat therapy has been practiced for thousands of years as part of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). The practice is known as "tui na" and involves using massage techniques to stimulate the flow of qi (life force) and promote sweating. TCM practitioners believe that sweating helps to release toxins and restore balance to the body.
The use of sweat therapy has also been documented in ancient India, Egypt, and Mesoamerica, highlighting its widespread appeal across diverse cultures.
Modern Applications of Sweat Therapy
Sweat therapy continues to be practiced and explored in modern times, with growing recognition of its potential health benefits.
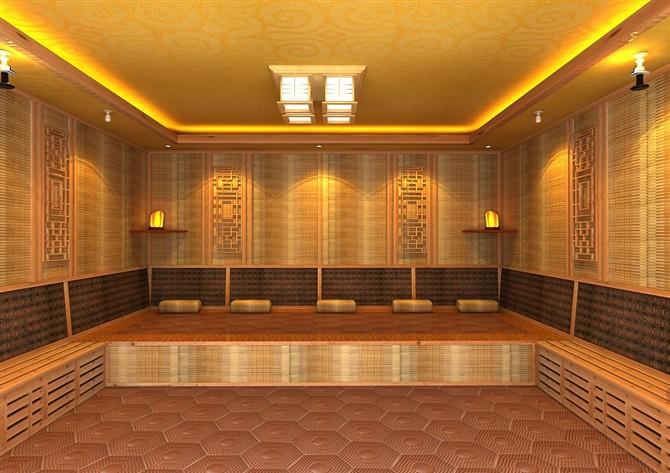

**Detoxification:**
Sweating is a natural detoxification process that helps to eliminate waste products and toxins from the body. By inducing sweating, sweat therapy can support the body's natural detoxification pathways and promote overall cleanse.
**Muscle Relaxation and Pain Relief:**
The heat generated during sweat therapy can help to relax muscles, reduce tension, and alleviate pain. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from muscle soreness, stiffness, or chronic pain conditions.
**Improved Circulation:**
Sweating increases blood flow to the skin, which can help to improve circulation throughout the body. This can have a positive impact on cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
**Stress Reduction and Relaxation:**
The warmth and soothing environment of a sweat therapy session can promote relaxation and reduce stress levels.

**Skin Health:**
Sweating can help to cleanse the pores and improve skin health.
**Immune System Support:**
Some studies suggest that sweating may have a positive impact on immune function by helping to eliminate toxins and stimulate the production of white blood cells.
**Mental Clarity and Focus:**
The heat and relaxation associated with sweat therapy can help to clear the mind, improve focus, and promote mental clarity.
Conclusion
The history of sweat therapy is a testament to its enduring value as a holistic approach to health and well-being. From ancient civilizations to modern times, sweat therapy has been recognized for its ability to promote detoxification, relaxation, and overall wellness. As we continue to seek natural and effective ways to enhance our health, sweat therapy offers a timeless practice rooted in wisdom and tradition.
转载请注明:成都会所桑拿-四川成都休闲桑拿推荐论坛! » 武汉休闲 » ## A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Rich History of Sweat Therapy
版权声明
本文仅代表作者观点,不代表成都休闲网立场。
本文系作者授权发表,未经许可,不得转载。